Weekly Ocean News
Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Salmon, sharks, and cod are suffering cognitive problems and disorientation from high carbon dioxide levels. Gases like this dissolve better in colder, deeper waters. The problem is particularly severe in northern estuarine waters, where fertilizer run-off has lowered oxygen levels. Via Phys.org
Crawfish, more commonly known as swamp crayfish, have spread from the marshes of the southeastern USA to every corner of the world. Researchers in South Carolina found that invasive crayfish populations had significantly lowered the number of dragonfly nymphs, their prey, and consequently mosquito larvae are on the rise without the dragonfly predators. Via National Geographic
UBC researchers looked at a list of 825 over-explored seafood species and determined that 60% of those marine fish species will be at risk of extinction if overfishing continues. Rays and sharks are most in danger. Active multinational fisheries management plans and combatting habitat loss from global warming would help reduce the startling trends. Via EurekAlert!
Fishing

UBC researchers looked at a list of 825 over-explored seafood species and determined that 60% of those marine fish species will be at risk of extinction if overfishing continues. Rays and sharks are most in danger. Active multinational fisheries management plans and combatting habitat loss from global warming would help reduce the startling trends. Via EurekAlert!
In Australia, bait traps made of chicken wire are used to catch snapper and yellowfin bream but frequently catch small sharks and rays instead. Researchers found that attaching small $5-10 magnets reduced bycatch by 30% and increased fish yields by the same amount. The magnets disrupt the food-finding electric senses of sharks, just like humans avoid a bad smell. The magnets, however, only emit a field of around 8 inches, so are unlikely to be strong enough to keep sharks away from long-line fishing. Via National Geographic
Global Warming
Due to the lack of sufficient ice melt in Lake Geraldine, the City of Iqaluit has introduced water restrictions and delayed opening businesses. The City of Iqaluit uses 1.4 million cubic metres of water each year, most of which is taken from the now frozen Lake Geraldine. While the city plans to pump water from neighboring rivers, it will not sustain the city’s growing population. Via CBC
Scientists in Alaska have identified another significant source of greenhouse gas emissions in the form of thermokarst lakes. These lakes form when rapidly warming soil melts ground ice. The permafrost at the bottom of the lakes melt, providing food for microbes that, in turn, produce methane. The release of methane from thermokarst lakes is significant, as methane is 30 times more potent than carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas. Via EurekAlert!
The kelp forests of the North-East Atlantic will experience a marked change as ocean warming continues. Cold-water kelp are showing less tolerance for warming seas, while warm-water kelp shows greater resilence. Warm-water kelp can provide a continuous supply of food, yet but won’t support the biodiversity of a cold-water kelp ecosystem. Via EurekAlert!
Plastics
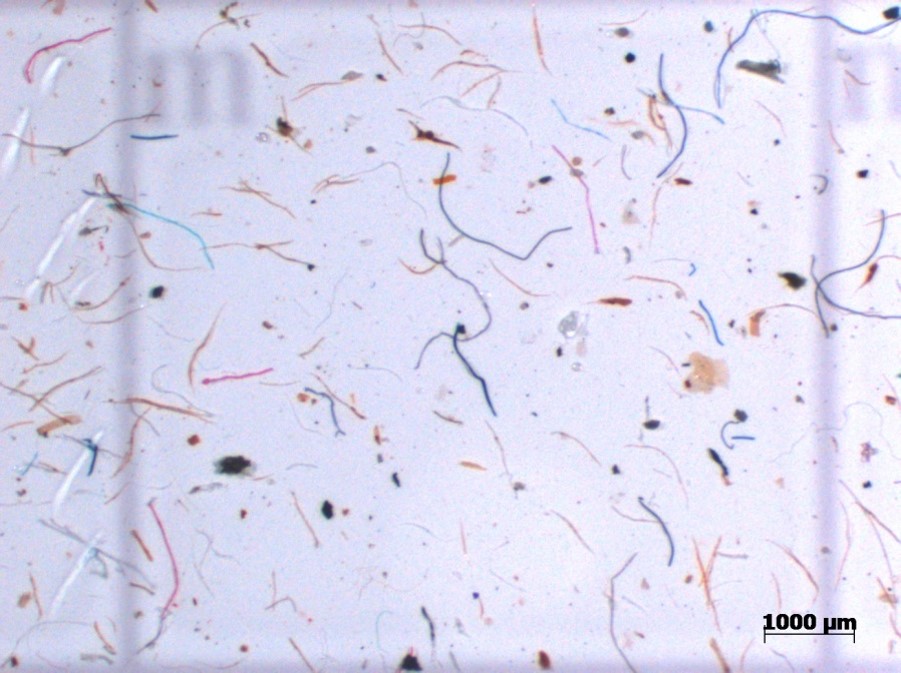
from the breakdown of larger pieces of plastic or textiles.
After a detailed study, scientists are pleading with humanity: Please stop flushing your contact lenses! Contact lenses improve the overall quality of life for some, yet pose problems in the marine environment. Contact lenses are of soft plastics that break up into microplastics in the ocean, rivers and lakes. Via BBC
Government Action
Spain’s constitutional crisis could impact the marine environment. Red coral is slow to grow and reproduce because it is prized by collectors, especially in east Asia, where the colour red is considered lucky. The secessionist Catalan government banned the collection of red coral along the coasts of northern Spain, but the Federal government, which has imposed direct rule on the region, has issued new licenses to collectors. Via Hakai Magazine
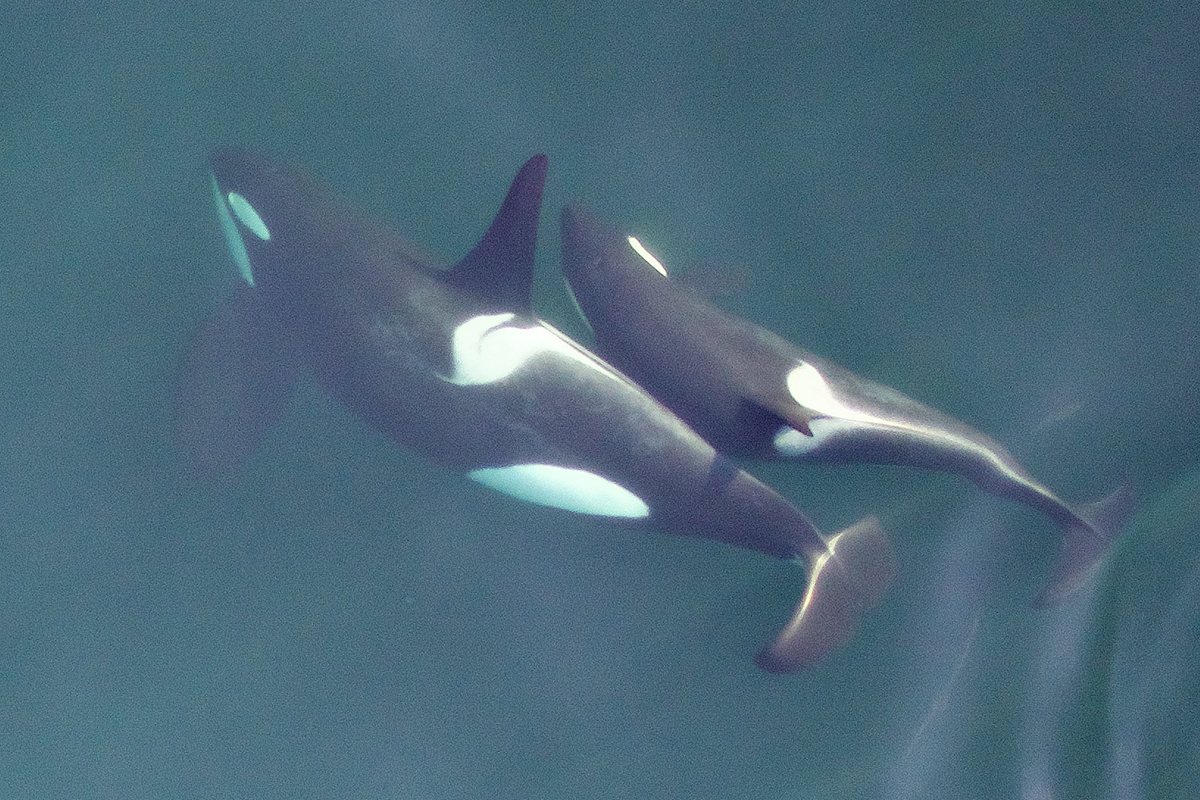

International agreements to phase out the use of chlorinated biphenyls and other persistent organic pollutants seems to be working. Research over the last 20 years shows a steady decline of these pollutants in the fat of Arctic marine mammal. While the concentration of flame retardants is still rising, these were only withdrawn last year and the ban will take many years to show in the blubber. Via Science Daily
The coastal municipalities of Delta and Surrey are drafting plans to protect homes and businesses from rising sea levels. It isn’t just the effect of global warming. Communities are aware that they are not prepared for a 100-year flood, like those in 1948 and 1894. The plans call for more dykes and pumping stations, which cost up to $3 billion, but the estimated damage from a flood on the scale of 1894 could cost upwards of $32 billion. A less costly option is a managed retreat from vulnerable areas, including 400 properties in Crescent Beach and up to 80% of farmland in Delta. Via Western Investor
Posted August 31, 2018 by Ocean Wise








