Le temps et le climat dans le monde
Comme l’océan absorbe la majeure partie du rayonnement solaire qui atteint la Terre, l’interaction entre l’océan et l’atmosphère contrôle le temps et le climat. Des changements dans l’océan ou l’atmosphère peuvent entraîner des modifications du climat.
L’énergie du soleil réchauffe notre monde, et l’océan absorbe la majeure partie de ce rayonnement solaire (chaleur). La raison en est complexe, mais nous pouvons la simplifier en trois points principaux.
Tout d’abord, l’océan peut absorber des quantités massives d’énergie sans que sa température ne change trop. En effet, l’eau a une capacité thermique élevée. Cela signifie qu’il faudrait une grande quantité d’énergie pour augmenter la température d’un litre d’eau d’un degré Celsius.
L’océan a un très grand volume et peut donc absorber une grande partie de la chaleur sans atteindre sa capacité thermique.
L’océan couvre environ 70 % de la surface de la Terre et dispose donc d’une grande surface pour absorber le rayonnement solaire.
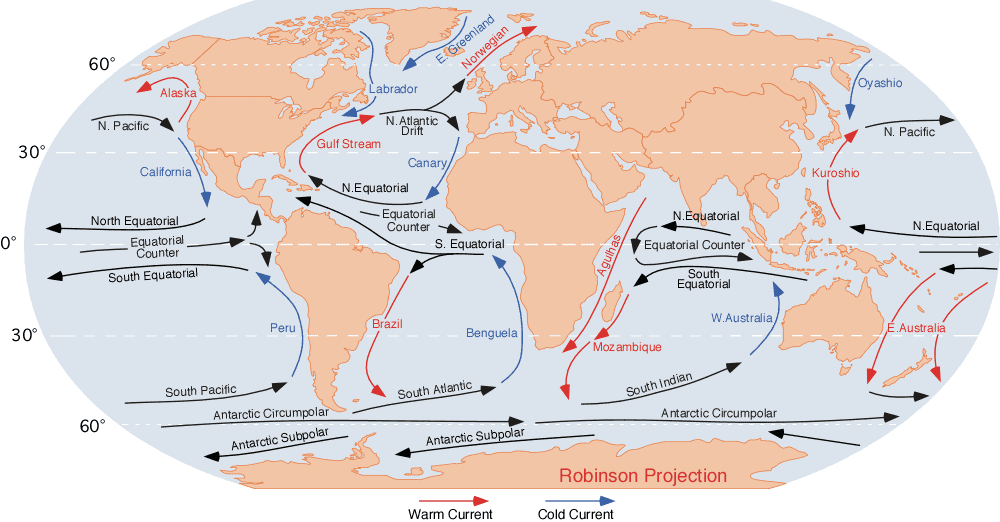
Le soleil chauffe la planète de manière inégale, ce qui crée des différences régionales et saisonnières de température et de pression. Ces différences, associées à la rotation de la Terre et à la convection (l’air froid s’enfonce et l’air chaud s’élève), entraînent un déplacement de l’air.
Les vents contribuent à déplacer les courants océaniques de surface, ce qui rend les climats des régions septentrionales comme l’Europe plus chauds et plus faciles à vivre.
En revanche, l’eau plus froide et plus salée, qui est plus dense, crée des courants plus lents et plus profonds dans l’océan. La circulation ou les courants océaniques déplacent l’eau et la chaleur autour de la planète, réchauffant les zones froides et refroidissant les zones chaudes.
L’océan exerce un tel contrôle sur le temps et le climat que nous pourrions même l’appeler notre “climatiseur”, car il régule et modère la température de l’atmosphère.

L’océan conditionne également l’air en absorbant l’excès de dioxyde de carbone (CO2). Il a absorbé environ 40 % du CO2 brûlé depuis le début de la révolution industrielle en 1775. L’augmentation des quantités de CO2 atmosphérique due à la combustion des combustibles fossiles entraîne des changements importants dans le climat et les systèmes océaniques, allant même jusqu’à modifier la chimie des océans.
Aujourd’hui, l’océan ne peut absorber qu’environ un tiers (33 %) de nos émissions de CO2 chaque année et il se réchauffe. À mesure qu’il se réchauffe, il peut absorber de moins en moins de CO2. Avec moins de CO2 dans l’océan, plus de dioxyde de carbone recouvre l’atmosphère comme une couverture chaude, emprisonnant la chaleur et isolant la planète.
Le réchauffement à long terme n’est qu’un des signes du changement climatique, mais il a un impact important qui fait lentement augmenter la température des océans, l’intensité des tempêtes, la fonte des glaces, l’élévation du niveau de la mer et la modification des régimes de salinité.
En connaissant les propriétés de l’eau et la façon dont la chaleur est absorbée ou libérée à travers les différents états de H2O, nous pouvons mieux comprendre les changements climatiques et océaniques. L’échange de chaleur entre l’atmosphère et l’océan est à l’origine du cycle de l’eau, de certains vents et des courants océaniques. Il influence également les conditions météorologiques.
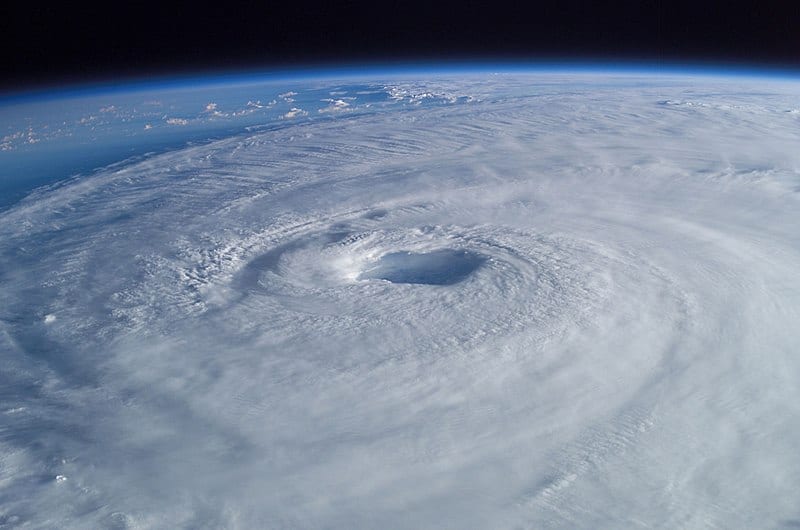

Les ouragans et les cyclones, par exemple, sont le résultat d’un échange de chaleur entre l’océan et l’atmosphère et vice-versa.
La plupart des pluies qui tombent sur la terre proviennent de l’eau évaporée de l’océan et les schémas mondiaux de pluie et de sécheresse, ainsi que les principaux phénomènes météorologiques, peuvent être attribués aux courants océaniques et aux températures de surface de la mer.
La circulation océanique redistribue la chaleur et l’humidité dans l’atmosphère. Les boucles de rétroaction qui relient l’océan, l’atmosphère, les conditions météorologiques et le climat peuvent avoir des conséquences inattendues.
Les phénomènes El Niño – Oscillation australe (ENSO) et La Nina constituent l’un des exemples les plus importants de l’influence des océans sur les conditions météorologiques. Nous entendons souvent ces termes dans les journaux télévisés ou sur les chaînes météo. L’ENSO est un changement occasionnel et irrégulier des vents et de la température de la surface de la mer.
Il s’agit d’un phénomène climatique qui passe de neutre à La Niña ou El Niño. Il se produit généralement dans l’océan Pacifique oriental et ses effets s’étendent à l’ensemble du globe.
El Niño est une phase de réchauffement avec une pression atmosphérique de surface élevée. La Niña est une phase de refroidissement avec une faible pression atmosphérique en surface. Les effets d’El Niño et de La Niña sont ressentis dans le monde entier.
Pendant une phase de La Niña (refroidissement), on peut s’attendre à de fortes pluies en Asie du Sud-Est, mais aussi à des conditions plus sèches que la normale dans le nord, en Alaska. La Niña déplace les trajectoires des tempêtes suffisamment loin vers le nord pour apporter des conditions hivernales plus humides que la normale dans les États du Midwest, ainsi que des étés chauds et secs.
Lors d’une phase El Niño (réchauffement), on peut s’attendre à des mois chauds et très humides d’avril à octobre, ce qui peut provoquer d’importantes inondations en Amérique du Sud.
Il est également susceptible de provoquer de fortes pluies dans l’ouest de l’Amérique du Nord. Il augmente le risque de tempêtes tropicales, de cyclones et d’ouragans parce qu’il s’agit d’un changement climatique plus chaud que d’habitude.Â
Au cours des dernières années, le nombre d’événements El Niño a augmenté et le nombre d’événements La Niña a diminué. Il faut davantage de temps d’observation avant de pouvoir détecter des changements importants ; cependant, de nombreux scientifiques pensent qu’El Niño est lié au changement climatique mondial qui se traduit par un réchauffement croissant de la planète.
Plus nous en savons sur la manière dont nous influençons ces grands processus que sont le temps, le climat et les océans, plus nous pouvons assumer la responsabilité de leur santé. Nous pouvons créer des solutions qui protègent les personnes, les lieux et les habitats vitaux. Des solutions telles que la réduction de notre empreinte carbone sont un bon point de départ.
Grâce à ces connaissances, les êtres humains peuvent travailler ensemble pour atteindre les objectifs de développement durable des Nations unies. Grâce à notre compréhension de l’océan, nous pouvons travailler à la réalisation de ces objectifs :
14.2 D’ici à 2020, gérer et protéger durablement les écosystèmes marins et côtiers afin d’éviter des effets néfastes importants, notamment en renforçant leur résilience, et prendre des mesures pour les restaurer afin que les océans soient sains et productifs.
14.5 D’ici à 2020, conserver au moins 10 % des zones côtières et marines, conformément au droit national et international et sur la base des meilleures informations scientifiques disponibles.
14.C Renforcer la conservation et l’utilisation durable des océans et de leurs ressources en mettant en œuvre le droit international tel qu’il est reflété dans la CNUDM, qui fournit le cadre juridique pour la conservation et l’utilisation durable des océans et de leurs ressources, comme le rappelle le paragraphe 158 de L’avenir que nous voulons.
Posted January 17, 2022 by Rosemary Newton



